In the world of data-driven marketing and customer relationship management, three key platforms often come up: Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Data Management Platforms (DMP), and Customer Data Platforms (CDP). While these platforms share the common goal of helping businesses better understand and engage with their customers, they serve distinct purposes and operate in different ways. Understanding the differences between CRM, DMP, and CDP is essential for choosing the right solution to meet your business needs.
The Differences Between CRM, DMP, and CDP
1. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM systems are designed to manage and nurture relationships with existing customers. CRMs primarily focus on storing and organizing customer data related to sales, customer service, and support interactions. These systems help businesses track customer history, manage sales pipelines, and improve customer service.
Key Features:
- Customer Interaction Tracking: CRMs store detailed records of customer interactions, including emails, phone calls, and meetings.
- Sales Management: CRMs help manage the sales process, from lead generation to closing deals.
- Customer Support: CRMs enable businesses to manage customer inquiries and support tickets, improving response times and service quality.
Use Case: CRMs are best suited for businesses focused on maintaining and improving relationships with existing customers, particularly in sales and support functions.
2. Data Management Platform (DMP)
DMPs are primarily used for managing and analyzing large volumes of anonymized data from various sources, such as cookies, online ads, and third-party data providers. These platforms are often used for targeted advertising and audience segmentation.
Key Features:
- Audience Segmentation: DMPs enable businesses to create detailed audience segments based on online behavior, demographics, and interests.
- Third-Party Data Integration: DMPs aggregate data from external sources, such as ad networks and data brokers, to enhance audience profiles.
- Anonymized Data: DMPs work with anonymized data, meaning that personal information like names or email addresses is not stored.
Use Case: DMPs are ideal for businesses focused on digital advertising and marketing campaigns, particularly those that rely on third-party data for targeting and audience building.
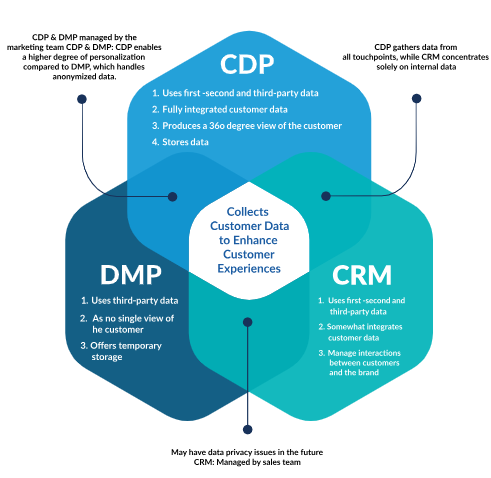
3. Customer Data Platform (CDP)
CDPs are designed to unify and manage first-party customer data across multiple channels, creating a single, comprehensive view of each customer. Unlike DMPs, CDPs handle identifiable data, allowing for personalized marketing and customer engagement.
Key Features:
- Data Unification: CDPs consolidate data from various touchpoints, such as websites, mobile apps, and email systems, into a unified customer profile.
- Real-Time Personalization: CDPs enable businesses to deliver personalized content and experiences based on real-time customer behavior and preferences.
- Customer-Centric Data Management: CDPs manage first-party data, ensuring that businesses can use customer information ethically and in compliance with privacy regulations.
Use Case: CDPs are best for businesses looking to enhance customer engagement through personalized marketing and a comprehensive understanding of customer behavior.
Key Differences
- Data Types: CRMs focus on customer relationship data, such as purchase history and customer interactions; DMPs work with anonymized third-party data for audience targeting; CDPs handle first-party, identifiable data to create unified customer profiles.
- Purpose: CRMs are designed to manage ongoing customer relationships and support; DMPs are geared toward audience segmentation and digital advertising; CDPs focus on personalized marketing and customer engagement across channels.
- Scope: CRMs are limited to known customers and interactions within a business’s ecosystem; DMPs operate in the realm of external data and are used for broad audience targeting; CDPs bridge the gap by unifying customer data from multiple sources and enabling personalized engagement.
Also Read: WhatsApp Marketing Campaign: A Powerful Strategy for Building Customer Engagement
Conclusion
While CRM, DMP, and CDP platforms each play a vital role in data-driven marketing and customer management, they serve different functions and are best suited to specific use cases. CRMs are essential for managing customer relationships, DMPs excel in targeted advertising, and CDPs offer a comprehensive approach to personalized marketing by unifying customer data. Understanding these differences will help you choose the right platform to optimize your marketing and customer engagement strategies.
By partnering with ProPS, you can unlock the full potential of your customer data, driving more effective marketing campaigns, increasing customer loyalty, and ultimately achieving better business outcomes. Let ProPS guide you in leveraging a CDP to transform your marketing efforts and stay ahead in a competitive landscape.
