Points of this article:
- Operational Distinctions: B2C relies on intermediaries like retailers to reach customers, while D2C eliminates middlemen, allowing brands to sell directly through their platforms and maintain full control over the customer journey.
- Data and Personalization: D2C brands gather first-party data directly, enabling personalized marketing and deeper customer insights, whereas B2C brands depend on limited data from intermediaries.
- Customer Relationships and Loyalty: D2C fosters direct engagement, stronger relationships, and greater brand loyalty, while B2C often struggles with limited direct interaction and customer retention.
In the world of commerce, business models are continually evolving to meet the demands of modern consumers. Two prominent models that often get compared are Business-to-Consumer (B2C) and Direct-to-Consumer (D2C). While both models focus on selling products to end customers, there are distinct differences in how they operate, market, and engage with their audiences. Understanding these differences can help brands determine which approach best fits their business goals and customer needs.
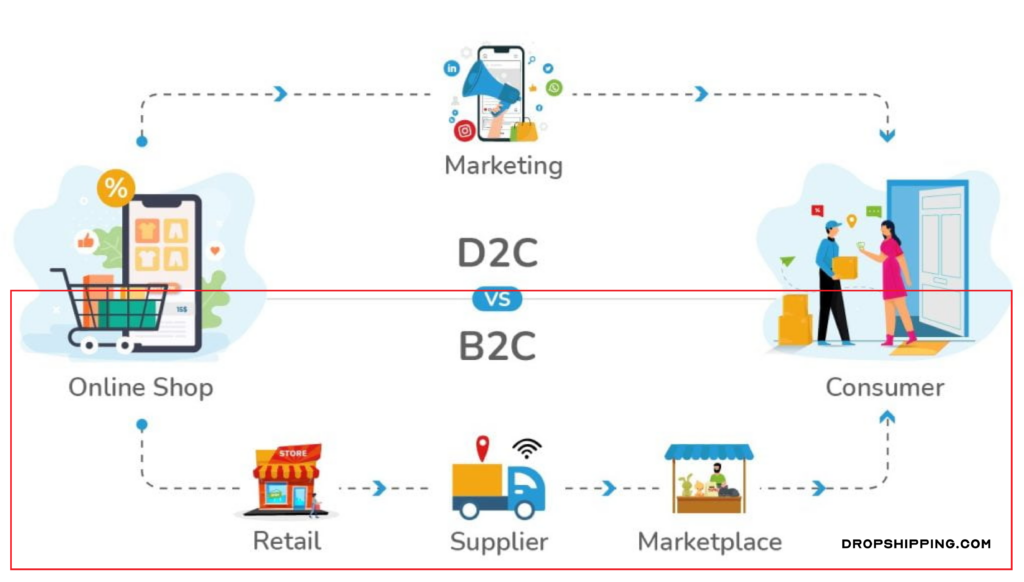
B2C (Business-to-Consumer) refers to the traditional model where businesses sell products or services to consumers through intermediaries, such as wholesalers or retailers. This model encompasses brick-and-mortar stores as well as online retail platforms where businesses rely on third parties to distribute their products to customers.
In a B2C model, businesses typically work with various channels—physical stores, eCommerce platforms like Amazon or Walmart, and sometimes other middlemen. The brand often has limited control over how the product is marketed or presented to consumers since third-party retailers handle much of the interaction.
D2C (Direct-to-Consumer), on the other hand, eliminates intermediaries entirely. In this model, brands sell their products directly to the customer via their own online store, social media platforms, or other digital channels. D2C marketing allows brands to own the entire customer experience, from product discovery and purchase to post-sale engagement and support.
D2C brands are in full control of how their products are marketed and delivered, which enables them to create highly personalized and targeted marketing campaigns. This direct connection also gives D2C brands access to valuable customer data, allowing them to better understand and respond to customer preferences.
The Differences Between B2C and D2C Marketing
Below are the fundamental distinctions that set B2C and D2C apart, highlighting their implications for businesses aiming to succeed in today’s competitive market.
1. Sales Channels
- B2C: Relies on third-party retailers, both online and offline, to sell products. Customers may purchase from large eCommerce sites or physical retail locations.
- D2C: Bypasses intermediaries and sells directly to the customer, usually through a brand’s own website or app. This direct relationship allows for more control over the sales process.
2. Customer Relationships
- B2C: The customer relationship is often managed by the retailer or intermediary, which limits the brand’s ability to engage directly with the consumer. Brands may have less influence over how customers perceive their products.
- D2C: Brands engage directly with their customers, giving them the ability to gather data, personalize marketing efforts, and build strong, lasting relationships. The direct interaction allows for better customer feedback and more tailored experiences.
3. Brand Control
- B2C: In the B2C model, retailers often control how the product is presented to the customer. This means that brands have less influence over product display, customer service, and pricing strategies set by retailers.
- D2C: In D2C marketing, the brand controls the entire process—from product design and pricing to how the product is marketed and delivered. This gives brands greater flexibility to differentiate themselves in the market.
4. Data Access
- B2C: Brands often rely on retailers for customer insights, but data collection is limited. Retailers may not always share critical information such as customer preferences, purchase history, or browsing behavior.
- D2C: With a direct sales model, D2C brands can collect first-party data from every customer interaction, enabling them to analyze customer behavior in-depth. This access to data provides invaluable insights for refining marketing strategies, developing new products, and improving the customer experience.
5. Customer Experience
- B2C: The customer experience in B2C is largely shaped by the retailer, from the product display in stores to the checkout process. Brands have less control over how the customer experiences their product.
- D2C: D2C brands curate the entire customer journey. They can create a seamless, consistent experience that aligns with their brand values, from the moment a customer visits the website to after-sales support. This allows for a more personalized and cohesive brand experience.
6. Marketing Strategies
- B2C: B2C marketing typically involves broad campaigns aimed at attracting as many customers as possible. Traditional advertising methods like TV commercials, print ads, and in-store promotions are common, often with less personalization.
- D2C: D2C brands often rely heavily on digital marketing strategies like social media campaigns, influencer marketing, and personalized email outreach. These brands use data to create highly targeted, customer-centric campaigns that speak directly to individual preferences.
7. Customer Loyalty and Retention
- B2C: Since B2C businesses often rely on intermediaries to manage customer interactions, building customer loyalty can be challenging. Customers may feel more attached to the retailer than to the brand itself.
- D2C: D2C brands can foster stronger loyalty by creating personalized experiences, offering exclusive deals, and directly addressing customer needs. This allows for greater brand affinity and repeat business as customers feel a closer connection to the brand.
Which Model Is Better for Your Business?
Choosing between B2C and D2C marketing depends on the nature of your business, your goals, and your resources.
- B2C is a good fit for brands that want to reach a broad audience through established retail networks. It’s ideal for companies that prefer to focus on product development while leaving distribution and customer management to retailers. B2C also offers access to larger distribution channels, which can help boost visibility and sales volume quickly.
- D2C is best for brands that want more control over their customer relationships, data, and brand narrative. It’s an excellent model for companies that are comfortable with managing their own eCommerce platforms and want to create a unique, personalized experience for their customers. D2C also allows brands to keep higher profit margins by cutting out middlemen and provides more agility to adapt to customer preferences.
In conclusion, while both B2C and D2C have their unique advantages, the rise of eCommerce and digital marketing has given D2C brands a competitive edge by allowing them to engage more directly and personally with their customers. Brands should carefully assess their goals and capabilities to choose the model that best fits their business strategy.
With ProPS, you can seamlessly navigate the complexities of D2C marketing and unlock the full potential of your brand.
